Human Health
Human health could be affected by many factors. Diseases caused by microorganisms are critical because of their potential to spread globally rapidly.
antimicrobial-resistant
Diseases
Many microorganisms have become resistant to almost all known antimicrobial, including last-resorts ones.


Animal Health
It is
well-established that animals
form an
important reservoir of pathogenic
organisms
that can be transmitted to humans
via direct
or indirect contact.
intensive antibiotic use
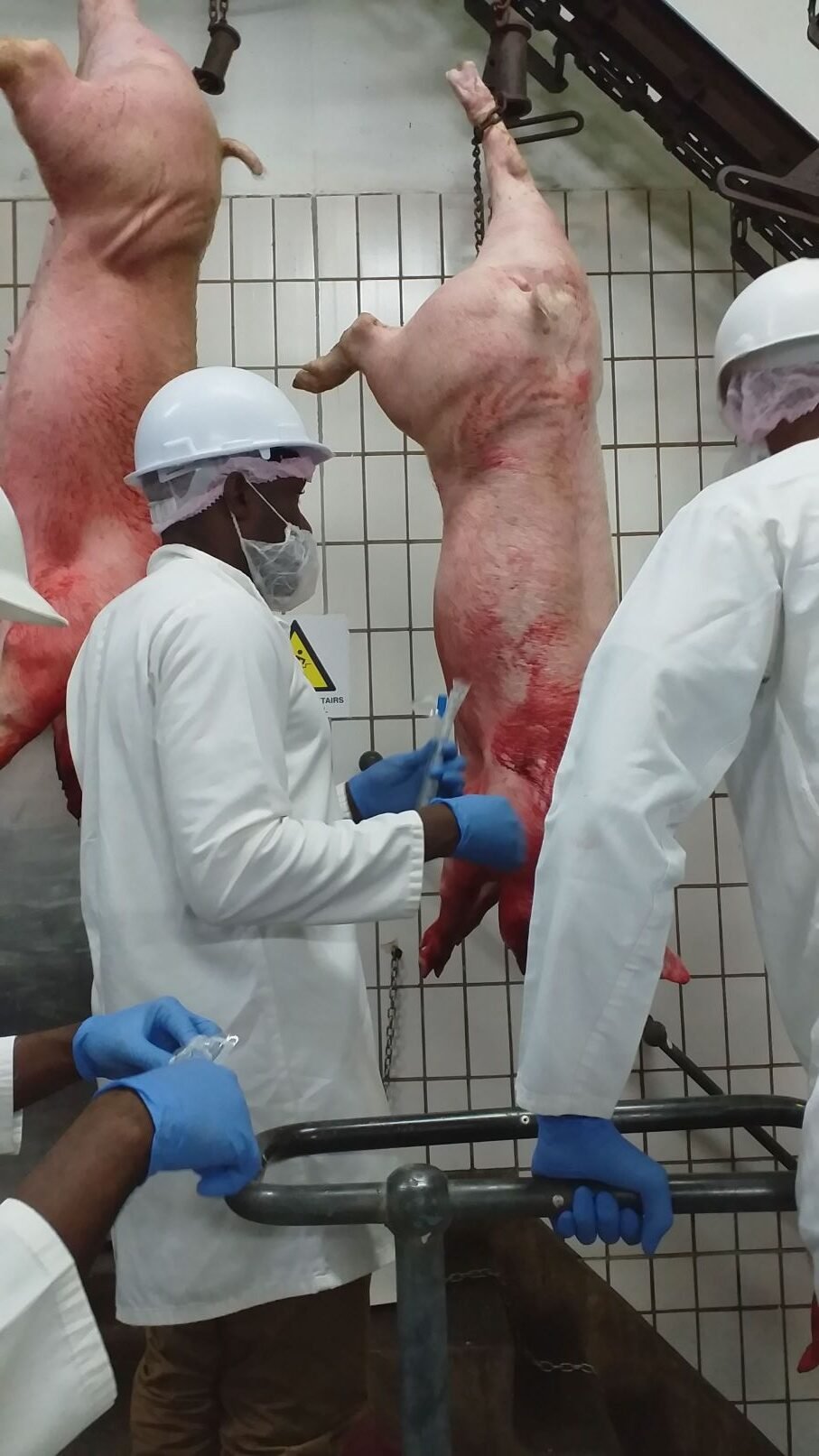
The growing need for animal protein and its associated products has caused an upsurge in intensive animal farming.


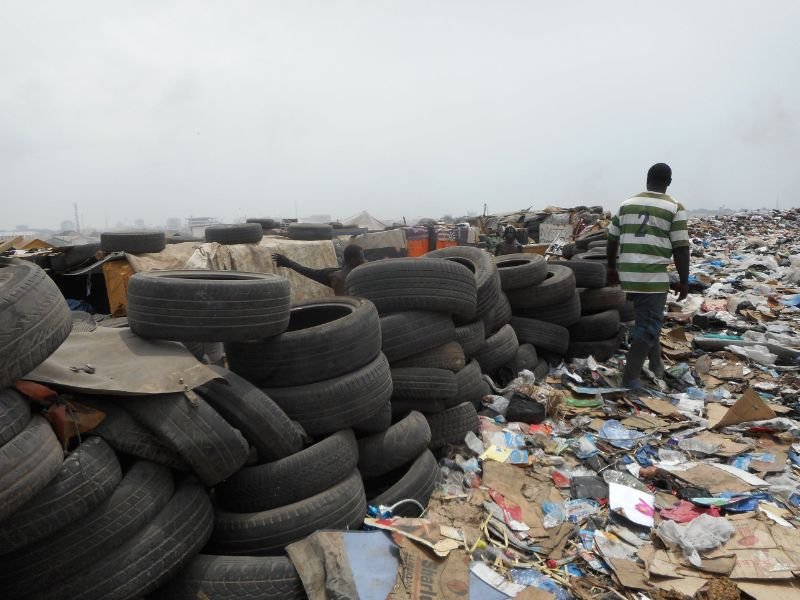
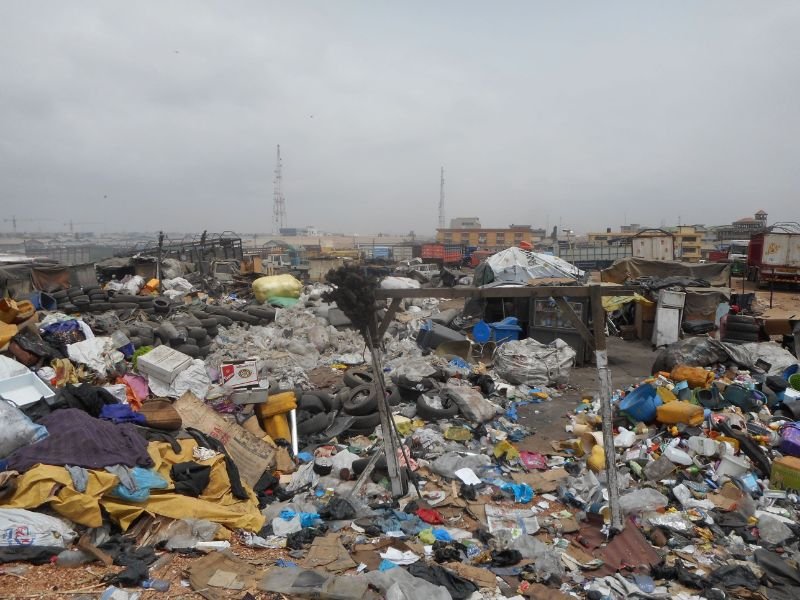
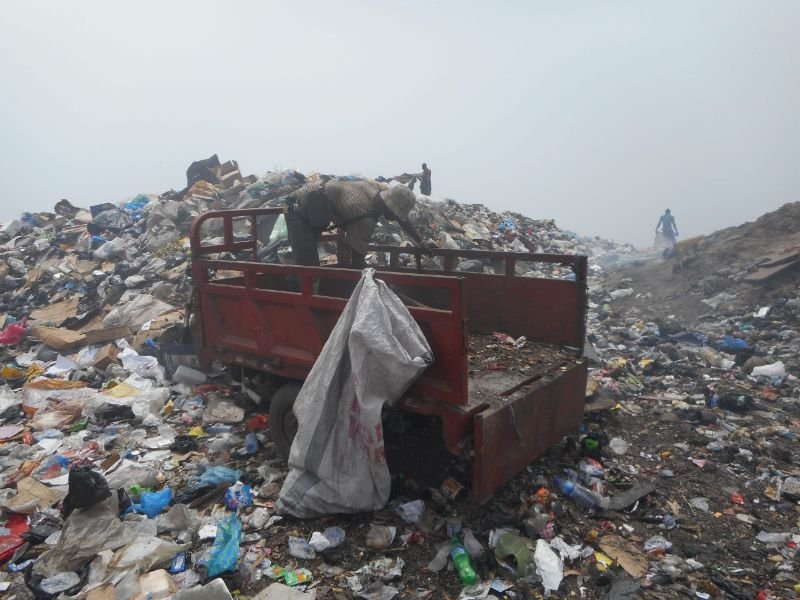
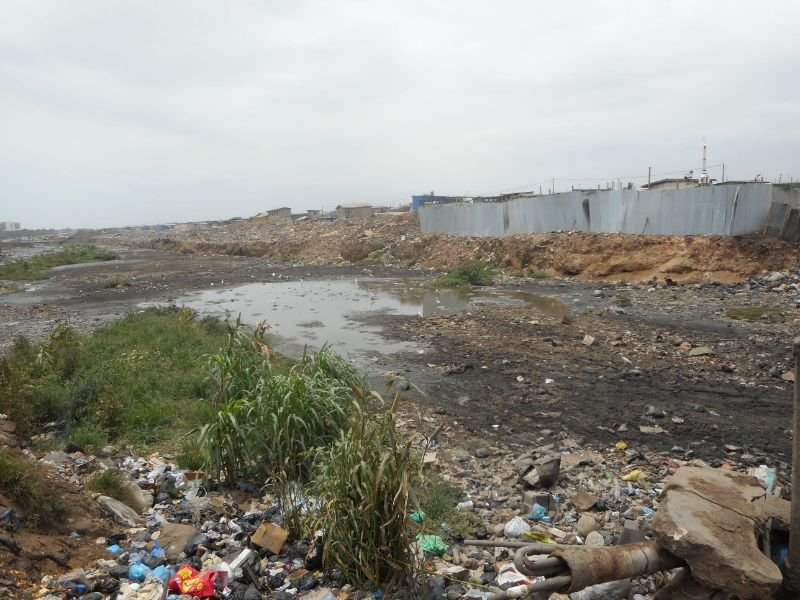
Environmental
Health
The World Health
Organisation has
indicated that a healthy
environment could
prevent almost 25% of the
global disease burden.
pollutants affect biodiversity
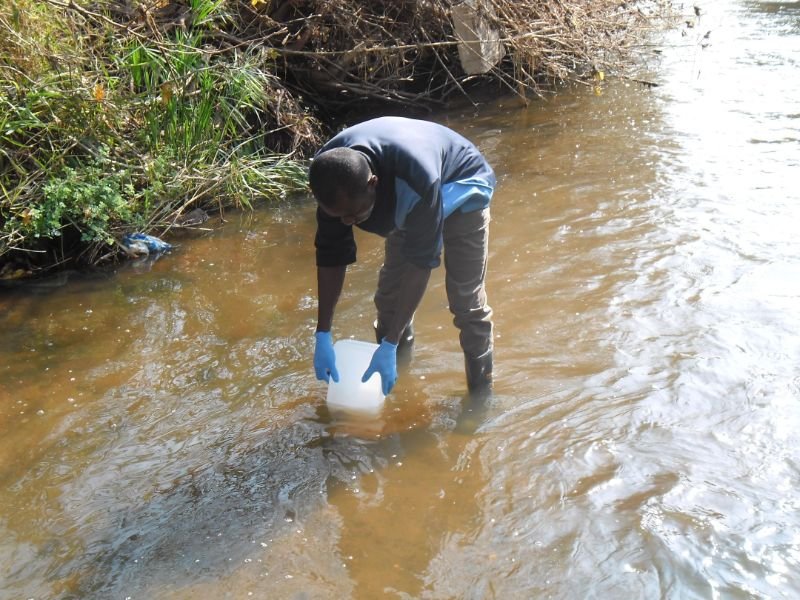
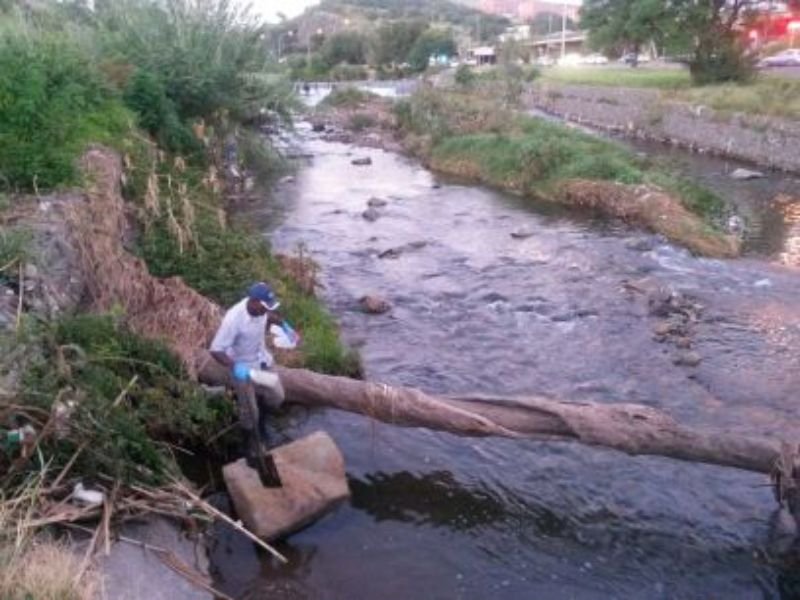
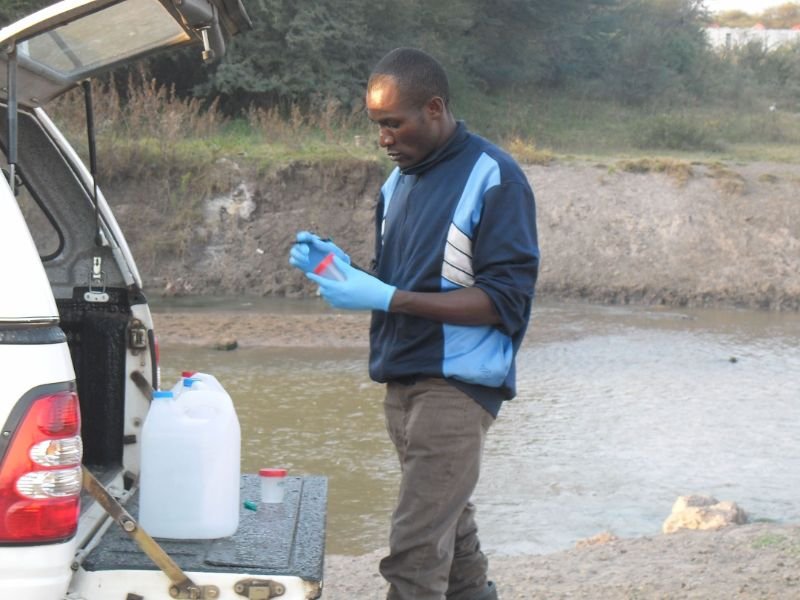
ERF investigates how humans and animals impact the environment and the implication of polluted environments on human health.


One Health
Human-animal-environmental health
is a trio
that can not be separated
Culture-
Dependent &
Independent Techniques
ERF conducts research to establish the link between human, animal and environmental health, to inform policy on curbing human diseases,
Let's Join To Build Towards One Health
“ONE HEALTH” can be achieved if the world works together, through projects and research initiatives exploring the triad, which is….
- Human Health
- Animal Health &
- Environmental Health
Environmental Health
The World Health Organisation has indicated that a healthy environment could prevent almost 25% of the global disease burden. However, the environment is continuously affected by natural and anthropogenic activities.
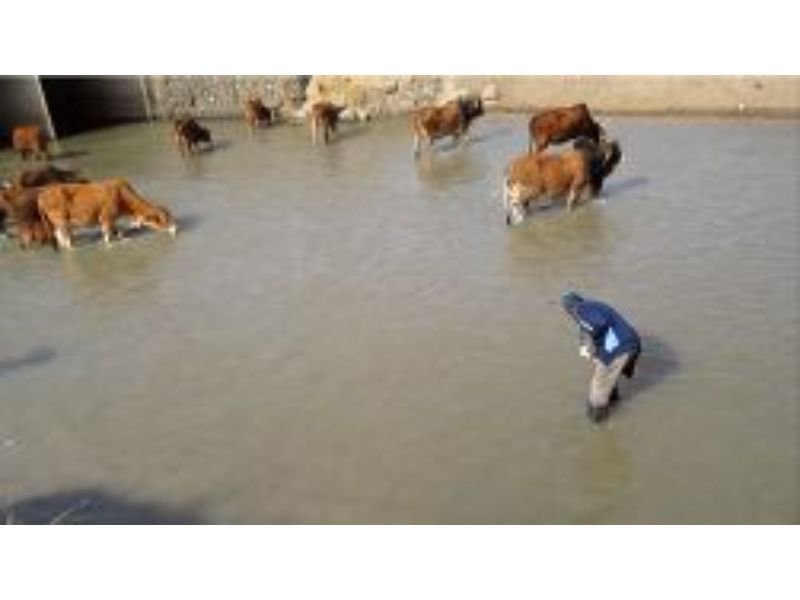
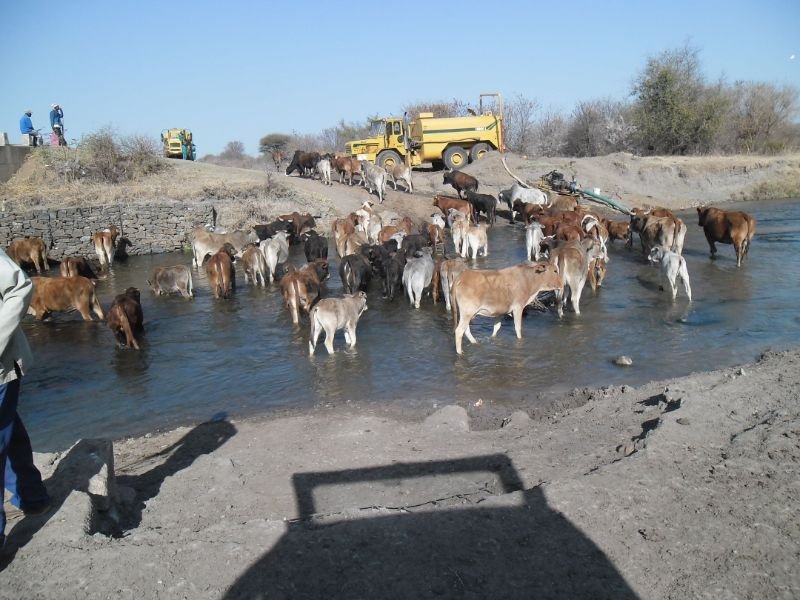
Animal Health
The growing need for animal protein and its associated products has caused an upsurge in intensive animal farming. However, this farming method involves growing many animals within a confined area, which stresses them, lowering their immunity.
Human Health
Human diseases are as old as creation and have lived with humans throughout the centuries. However, changing climatic conditions, changing human behaviours, rapid population growth and industrialisation have led to the emergence of new infections and the re-emergence of once-forgotten ones.
Abdalla et al., 2022
Antibiotic-resistant diarrhoeagenic E. coli pathotypes were isolated at all stages of the food-animal production line, from the farm to the final product, indicating that food of animal origin could serve as reservoirs for transmitting these bacteria to humans, especially in occupationally exposed workers and via food.
Fatoba et al., 2022
Application of chicken manure as a natural fertiliser resulted in a significant increase in antimicrobial-resistant E. coli in fertilised soil compared to unfertilised soil.
Abia and Tekere, 2023
COVID-19 lockdown measures did not significantly increase the risk of infection from exposure to polluted waters in informal settlements in South Africa.
Do You Wish To Ask About The Work That We Do As ERF ?
Please fill in the form and our team will engage with you through the contact information you left us.